What is cloud computing? #
Cloud computing is the provision of services over the internet (‘the cloud’), whether software, storage, infrastructure, databases, networking, analytics or intelligence, on demand with a subscription-based pricing system. It is basically anything that can be hosted over the internet for customers to access.
Cloud services remove the upfront costs and complexity of deploying IT infrastructure for organisations, making it cost effective, scalable and flexible, and easy to roll out and adopt. Organisations just pay for the resources they require.
What are the main types of cloud computing services? #
What is SaaS? #
In a Software as a service (SaaS) environment, applications and software are hosted on cloud servers and users access them via the internet through a subscription-based license model.
This makes SaaS applications very appealing to organisations as they don’t have to pay for the hardware, storage, maintenance or upgrades, meaning they save time, money and resources. SaaS applications can also be accessed from multiple devices and easily scaled up or down on demand.
Common SaaS solutions include Microsoft Office 365, Salesforce, HubSpot, MailChimp, Zendesk etc.
What is PaaS? #
Platform as a service (PaaS) provides organisations and developers with an environment to build and roll out applications and services in the cloud.
As PaaS is hosted in the cloud by a provider, organisations do not have to incur the costs of the hardware, hosting, software and tools. Instead they pay for the things, such as development tools, infrastructure and operating systems needed to build, test, deploy, host and maintain the applications over the Internet.
What is IaaS? #
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) provides compute resources, such as servers, storage and networking equipment, over the internet on a pay-as-you-go basis.
A cloud service provider provides and manages the infrastructure in a virtualised environment, and customers simply pay a subscription fee for the resources that they require to install, configure and manage their IT systems and applications.
This makes it easy for organisations to scale up or down to meet current demands, making it a very cost-effective solution.
What is iPaaS? #
Another cloud computing service that is experiencing greater demand is Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) – a dedicated cloud-based integration solution.
iPaaS provides a fully managed, multi-tenant cloud integration platform that can connect and integrate a variety of applications, data and processes in real time and in practically any combination across all operating environments, whether this is cloud-to-cloud integration, on-premises to cloud integration (hybrid) or on-premises to on-premises integration.
iPaaS removes many of the costs usually associated with data integration and business process automation, as all the tools and connectors are hosted, upgraded and maintained by the vendor, meaning that organisations can concentrate on core business strategies.
How does cloud computing work? #
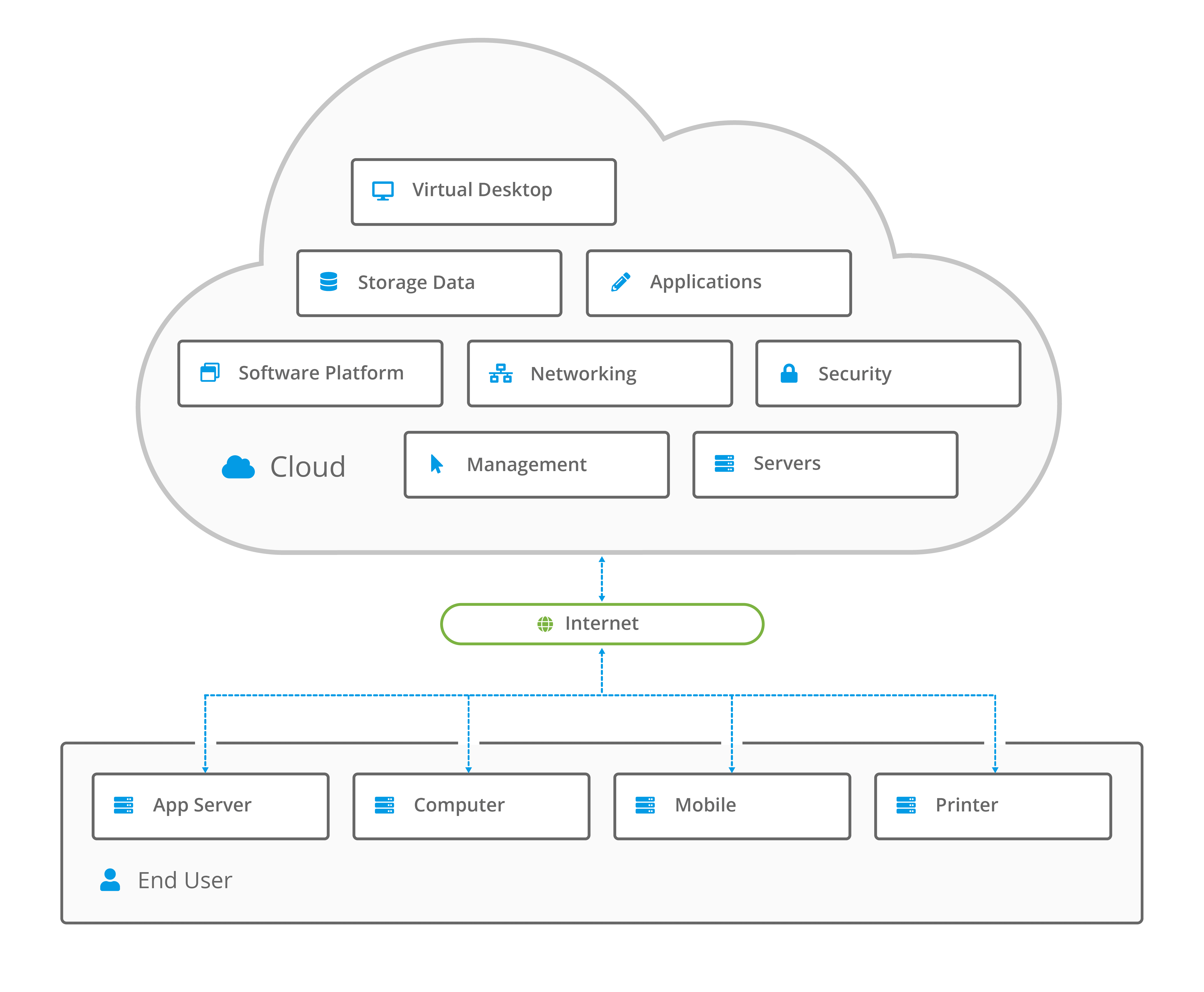
There are two core elements of cloud computing architecture which are the front-end platform and the back-end platform.
The front-end platform is the customer-facing graphical user interface, such as a client or application, that enables users to access the cloud-based services and/or resources.
The back-end platform contains all the elements that enable providers to deliver a cloud-based product or service, such as the databases, resources, the application, storage, security, management tools and central servers.
The central server uses software and middleware to manage the connectivity between the front end and the backend, and follows protocols to facilitate the transfer of data.
This is all made possible thanks to technology known as virtualisation. This technology enables the creation of a simulated, virtual computer, known as a virtual machine (VM), which is a software container that includes an operating system and application, and acts as if it has its own hardware.
Cloud computing providers can create multiple virtual machines on a single, partitioned server, which act independently of each other, meaning they can and run several operating systems and applications whilst using the same resources of the physical machine.
As a result, cloud providers can offer customers the ability to rent services, such as SaaS, PaaS and IaaS, rather than owning the infrastructure and data centres required.
Why is it called the cloud? #
‘The Cloud’ is basically a metaphor or bit of jargon that has simply been adopted by the wider IT industry to represent the internet and hosted services.
The term, which was really brought to prominence by Google’s Eric Shmidt at a conference in 2006, actually goes a lot further back, even before a company called NetCentric tried to trademark the name in 1997.
When telecoms engineers were drawing flowcharts and network schematics to explain and detail IT infrastructure, the infrastructure that made up the network were often represented by a cloud symbol. They were inferring that the location and structure of the network was irrelevant; it was just a collection of resources that could be accessed and the customers didn’t really need to know much more about it.
The cloud symbol was subsequentially used to represent the internet.
Ever since then, any computing resources that were described as only being accessible via the Web were defined as cloud computing.
What are the main cloud deployment models? #
There are a number of different deployment models available which are determined by where the cloud servers are located and who manages them.
What is public cloud? #
A public cloud is a platform hosted by a third-party over the internet that provides cloud computing services to anyone that wants to purchase them. Multiple companies will often share the same servers in one or more data centres, known as multitenancy, although each will be allocated their own secure database and virtual machine.
The most popular public clouds include Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, IBM Cloud, Microsoft Azure etc.
What is private cloud? #
A private cloud is a data centre, server or distributed network that is owned, managed and used solely by one single organisation – a single-tenant environment that doesn’t share its resources and has isolated access.
What is hybrid cloud? #
A hybrid cloud is an environment in which applications and services are run on a combination of a private cloud, public cloud and, quite often, on-premises legacy servers.
Each service will be used for a particular function or task dependant on where the organisation wants to store data or which services it wants to use.
This environment provides organisations with the flexibility to easily scale up or down, as well as quickly switch between different applications if necessary.
What is multi-cloud? #
A multi-cloud deployment involves using two or more public clouds from different vendors. For example, an organisation could use an IaaS solution from one vendor, but then use multiple SaaS products from other vendors.