Introduction #
This article provides basic guidance to using the Run External Program tool to run PowerShell scripts.
Procedure #
It is recommended you create the PowerShell script in a separate file, stored locally to the BPA Platform client. You can then use task variables to determine the file path and script file to call at task run-time.
You then use the Parameters table to specify the command line syntax which calls the script as Name | Value pairs, for example:
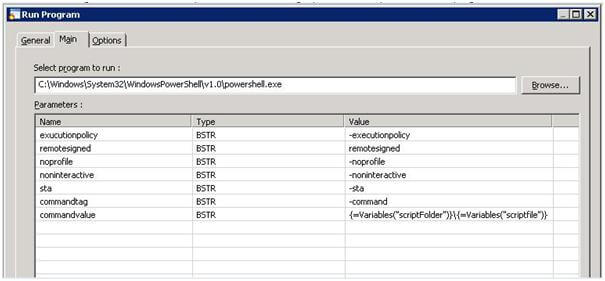
This example is a V2 PowerShell script. At task run-time, the PowerShell program is invoked and the following command run (note that example file paths and names have been used in place of the BPA Platform variables):
-executionpolicy remotesigned -noprofile -noninteractive -sta -command "c:\scripts\script1.ps"
–executionpolicy, remotesigned and -sta arguments will not work. Instead, run set-execution policy remotesigned first before running the command to call the script. For a detailed description of the security implications of setting the execution policy, refer to the PowerShell help (help set-executionpolicy).If you are unsure whether you are running v1.0 or v2.0, note the copyright message when you start up a PowerShell prompt — this will say (c)2006 for v1.0 or (c)2009 for v2.0.