What is the Run Microsoft Reporting Services Tool?
The Run Microsoft Reporting Services tool automates the running of Microsoft Reporting Services (MSRS) reports.
Two modes are available for running a report as follows:
- Report Server Mode — An existing report located on a MSRS Report Server is run either on a scheduled basis or based on an event. A connection to the server is set up through Global Configuration which includes the authentication details necessary to access the report.
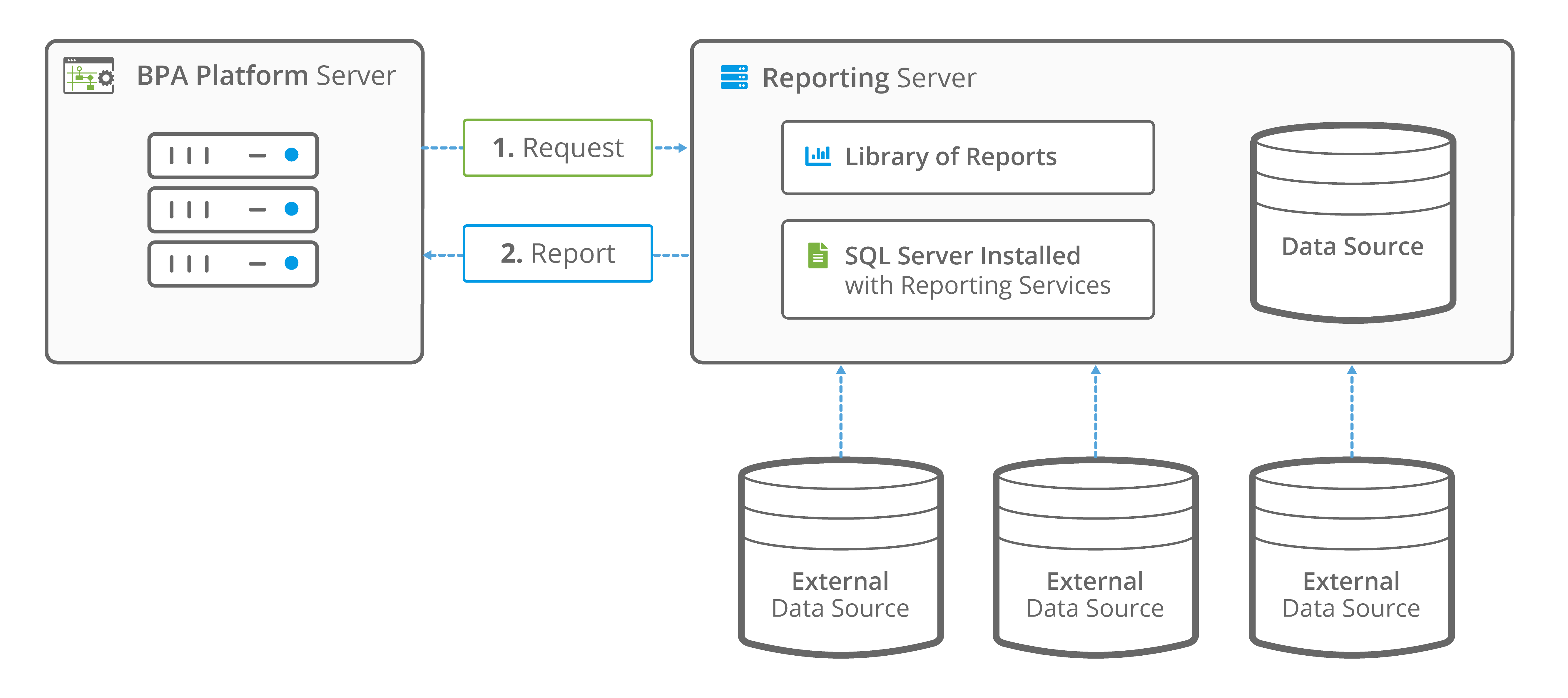
- Local Mode — A report is imported into BPA Platform which enables it to be run locally. A major benefit of doing this is that you are able to use dynamic data provided by other task steps, such as Database Query (ODBC), or configured as task or step Variables that can be passed to the report at task run-time. The data can then be used to run a report once or many times.
The report data exposed by the step can be “delivered” by Output steps such as Send Email (SMTP), Transfer File (FTP), or Save File, and then used to present sophisticated management information, delivered via email or fax, or published to form part of web or intranet content.
New reports are designed in the Microsoft Reporting Services designer environment, so experienced users of this application are able to produce a new report or modify an existing one, and integrate it with BPA Platform.

White Paper - Run Microsoft Reporting Services
Microsoft Reporting Services Tool Features
- Reports on Report Server are securely accessed via BPA Platform
- All the power of the Microsoft Report Server at your disposal
- Import and use existing reports
- Map dynamic data to the report and any nested sub-reports as run-time parameters
- Data security parameters passed to the report at run-time
Microsoft Reporting Services Tool: Working with Other Tools
The Run Microsoft Reporting Services tool can interact directly with the following tools:
Consuming from Other Tools
Run Microsoft Reporting Services can consume objects outputted by the following tools:
| Icon | Tool Name | Tool Category |
|---|---|---|
| Database Query (ODBC) | Input and Data Connectors | |
| Database Query (OLEDB) | Input and Data Connectors | |
| Import Flat File | Input | |
| Import XML Document | Input | |
| Retrieve Text Message | Input | |
| Convert Recordset to XML | Format | |
| Convert XML to Recordset | Format | |
| Transform Data | Format | |
| Call Task | Execute | |
| Filter Data | General | |
| Web Service Connector | Data Connectors | |
| Applications Platform Connector | Data Connectors |
Objects Consumed
The following objects, outputted by the above tools, can be directly consumed by the Run Microsoft Reporting Services tool:
- Recordset — Tabular data from any BPA Platform tool capable of exposing such data (see above)
- XML — XML data from any BPA Platform tool capable of exposing such data (see above)
Exposing to Other Tools
The Run Microsoft Reporting Services tool outputs objects that can be consumed by the following tools:
| Icon | Tool Name | Tool Category |
|---|---|---|
| Print Document | Output | |
| Save File | Output | |
| Send Email (SMTP) | Output | |
| Transfer File (FTP) | Output | |
| Call COM Object | Execute | |
| Run External Program | Execute |
The type of output produced by a Run Microsoft Reporting Services step is not set in the tool step. The tool consuming the output determines the type of output produced. The available outputs vary depending on the mode of operation (local or server) and are limited by the consuming tool.
Print Output
A print output of the report is available in both local and server mode using the Print Document tool.
Email Output
Report outputs can be delivered using the Send Email (SMTP) tool and the available types differ depending on the mode and whether the output is required as an attachment or in the message body.
| Output Type | Local Mode | Server Mode | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Message Body | Attachment | Message Body | Attachment | |
| ATOM | ||||
| CSV | ||||
| EXCEL | ||||
| EXCEL OPEN XML | ||||
| HTML32 NOTE:Not available when using SQL Server 2019 and above with the Microsoft Report Server. | ||||
| HTML40 | ||||
| HTML5 NOTE: Only available when using SQL Server 2016 and above with the Microsoft Report Server. | NOTE: Only available where the email service supports it. | |||
| IMAGE | ||||
| MHTML | ||||
| PPTX NOTE: Only available when using SQL Server 2016 and above with the Microsoft Report Server. | ||||
| RGDI | ||||
| RPL | ||||
| WORD | ||||
| WORD OPEN XML | ||||
| XML | ||||
On the Advanced tab, click the Output Formats button to open the Run Microsoft Reporting Services dialog. Click the OK button to save the connection. The available output types will then be refreshed.
File Outputs
The Save File Tool can be used to save to a local file system and the Transfer File (FTP) tool to save to a remote server. For both tools, in local mode Excel, Image, PDF, Word formats can be output; Excel and Word Open XML formats are additionally available using SQL Server 2012. In server mode all of the above outputs can be saved (from the table above). The Call Stored Procedure (OLEDB) tool can also consume these outputs in these modes.
Connecting to a Microsoft Report Server
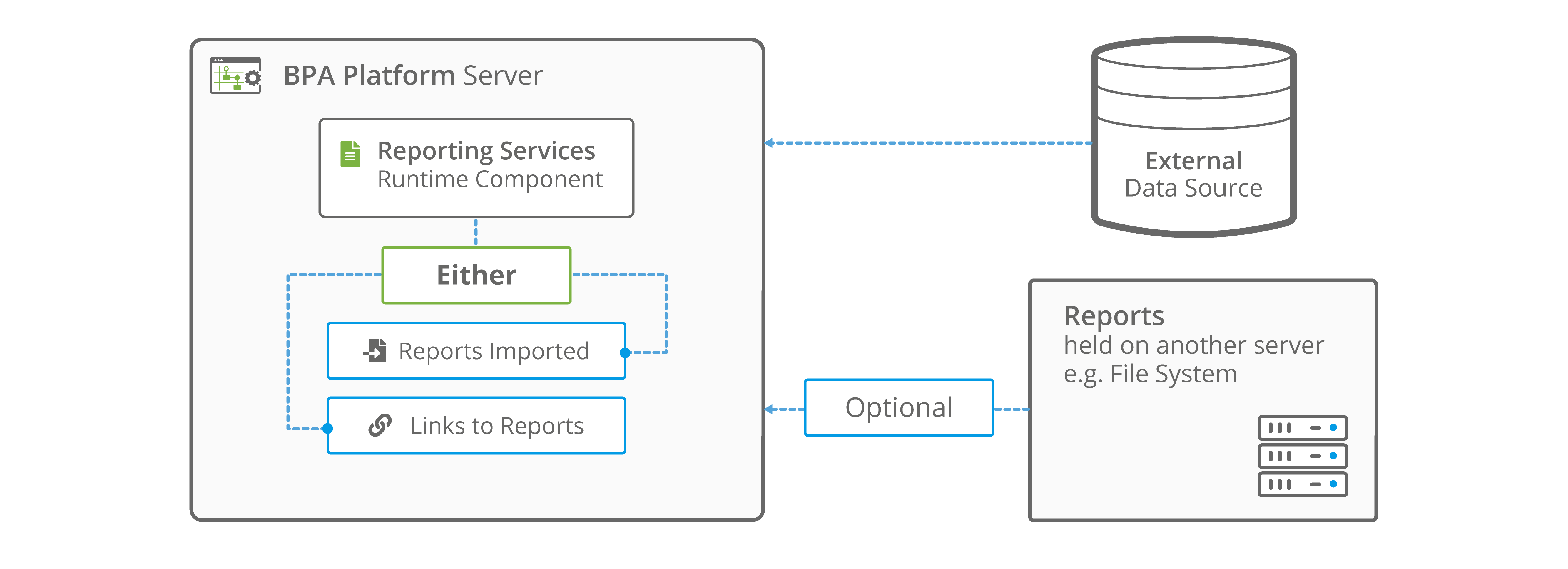
You can configure a connection to a Microsoft Report Server where the report is hosted, before adding a Run Microsoft Reporting Services task step. Alternatively, if a report is held locally, it can be either imported into BPA Platform or run from its existing location without having to configure a Microsoft Report Server connection.
You open the Run Microsoft Reporting Services Global Configuration dialog by either:
- Going to Manage > Tools > Format > Run Microsoft Reporting Services
- From the Task Manager, expanding BPA Platform > System > Tools > and double-clicking Run Microsoft Reporting Services in the Items List
Adding a Connection to a Report Server
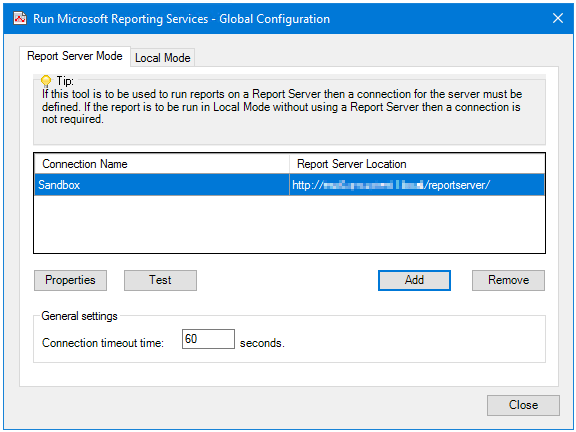
Use Properties and Remove to manage existing connections.
By default, the Run Microsoft Reporting Services tool drops the connection to the Report Server after 60 seconds of idle time. Adjust Connection timeout time as required.
Click Add to create a new connection.
Using a Local Report
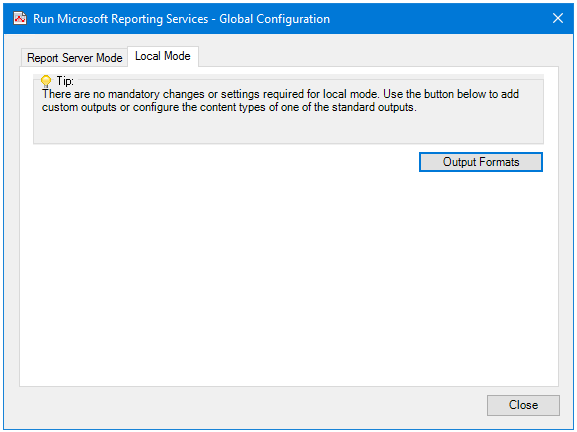
Although there are no mandatory global configuration requirements before using the Run Microsoft Reporting Services tool, you can add custom outputs or change the custom types of a standard output — click Output Formats.
Microsoft Reporting Services Tool: Step Configuration
To add a new Run Microsoft Reporting Services step to an existing task, you either:
- Click and drag the Run Microsoft Reporting Services icon from the Task Browser to the task Design area.
- From the task’s Design tab, right-click on empty space and select Add > Format > Run Microsoft Reporting Services.
For a detailed description of how to create new tasks, refer to the product help.
About the General Tab
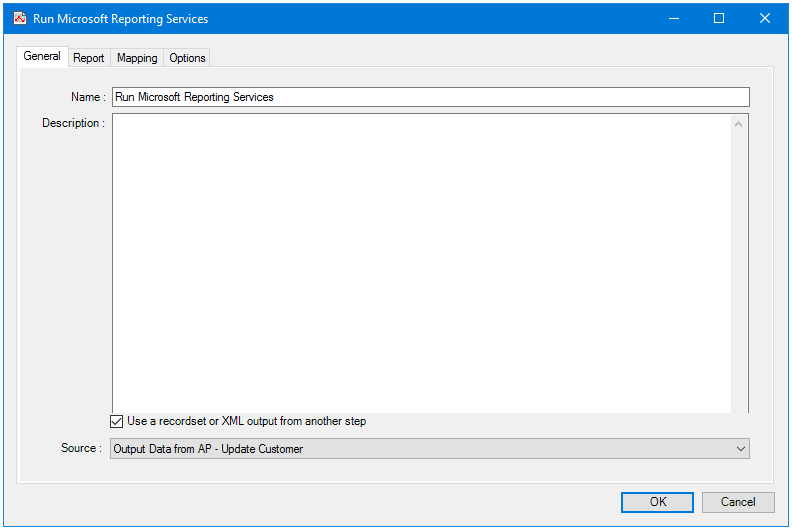
The General tab is used to enter the following details for the step:
- Name — Enter a meaningful name for the stepTIP: If this task instance makes use of two or more Run Microsoft Reporting Services steps, ensure the Name used is unique for each individual step.
- Description — If required, enter a description of this step
- Use a recordset or XML output from another step — Enable this parameter if recordset data or an XML document from a previous task step is required when creating the report
- Source — Contains all available inputs from steps previously created in the task
About the Report Tab
You use the Report tab to provide the report details for this task step. You have three options to running a report:
Run Report on a Microsoft Report Server
Choose this option when you have created a connection to a remote Report Server:
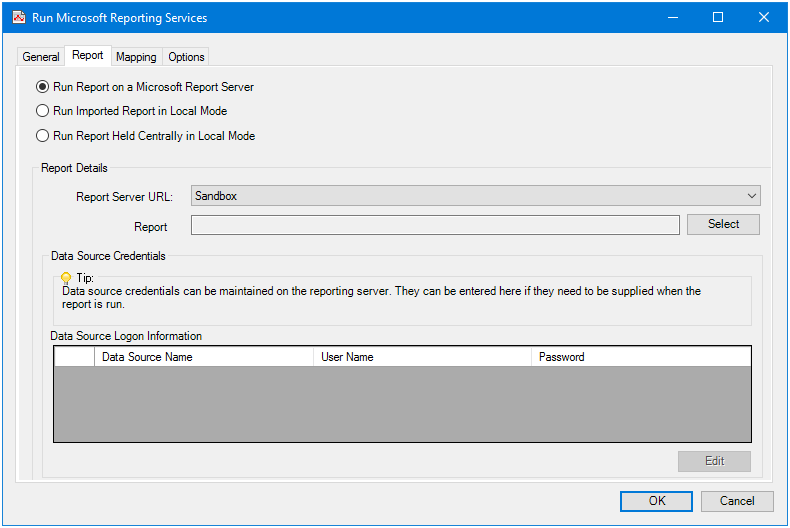
From Report Server URL, choose the relevant global connection for this task step. Click Select to choose the Report located on the server.
Whether database credentials are required at task run-time is dictated by the chosen report. If required at run-time, click Edit and enter the credentials (Username and Password) for all listed databases (Data Source Logon Information).
Run Imported Report in Local Mode
Choose this option to import a report from the local hard drive. If the report is located on a network drive, use Run Report Held Centrally in Local Mode.
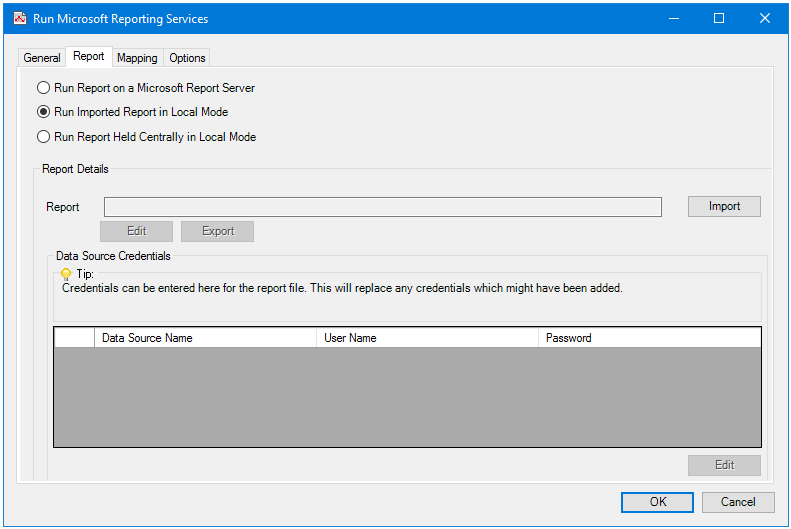
Click Import to select the report. The report is imported into the task step and cached. Subsequent changes to the report are not reflected in the imported report — you must re-import it to get the latest version.
Alternatively, click Edit to open the report in Microsoft Report Builder (locally installed only). You can then Export the report for use elsewhere or as a backup — the report is exported as a .rdlc file.
Whether database credentials are required at task run-time is dictated by the chosen report. If required at run-time, click Edit and enter the credentials (Username and Password) for all listed databases (Data Source Logon Information).
Run Report Held Centrally in Local Mode
Use this option to import a report from either another machine on the network or from a web server. To import a report held locally, that is on the same BPA Platform machine, use Run Imported Report in Local Mode.
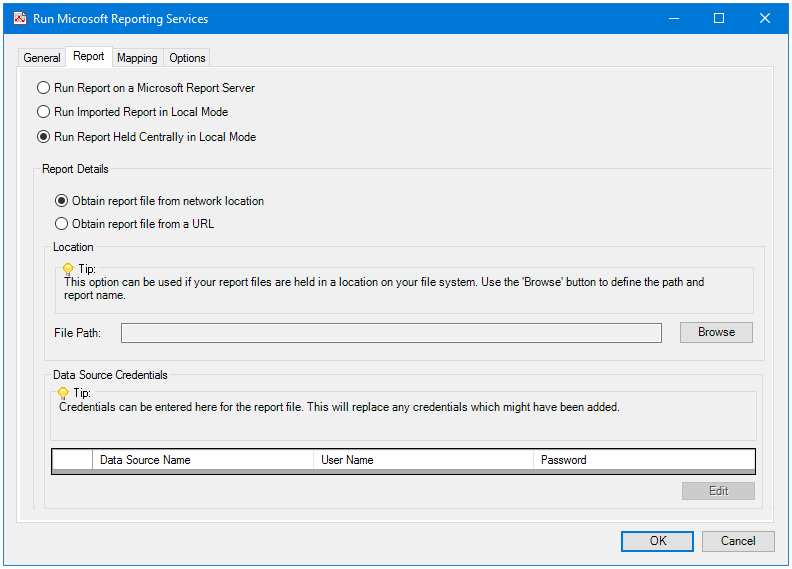
To import a report from another machine on the network, enable Obtain report from network location. Click Browse to locate and import the report. The report is imported into the task step and cached. Subsequent changes to the report are not reflected in the imported report — you must re-import it to get the latest version.
To import a report from a web server, enable Obtain report from a URL. Click Enter URL to locate and import the report. The report is imported into the task step and cached. Subsequent changes to the report are not reflected in the imported report — you must re-import it to get the latest version.
Whether database credentials are required at task run-time is dictated by the chosen report. If required at run-time, click Edit and enter the credentials (Username and Password) for all listed databases (Data Source Logon Information).
About the Mapping Tab
The Mapping tab uses the Data Transformation Component to map data provided by a previously configured Input step onto the parameters available for the selected report.
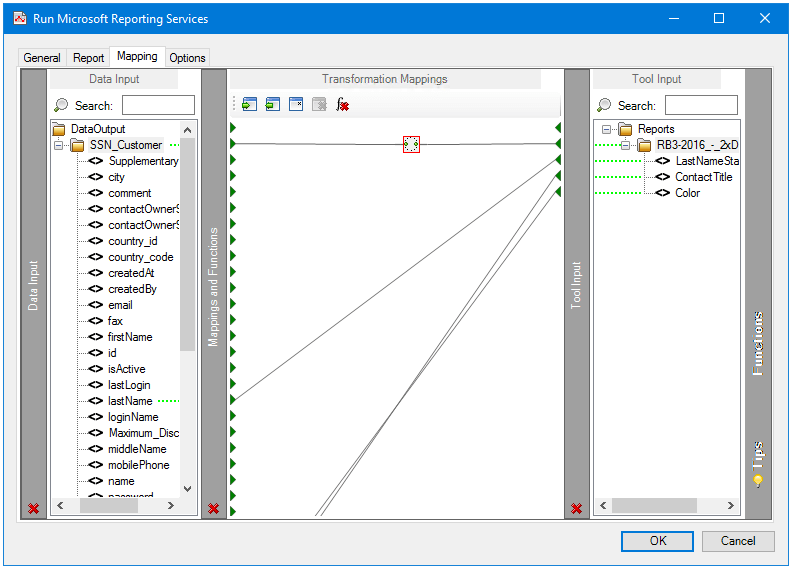
From here you can:
- Automatically map where input and output parameter names match
- Create mappings from a set of transform functions to change the data between input and output
- Use nested looping to support hierarchical data structures
- Import and export mappings so that they can be reused in other steps
For a detailed description of how to map data in this tab, refer to the product help.
About the Function Types
A number of functions are available with the data transformation layer:
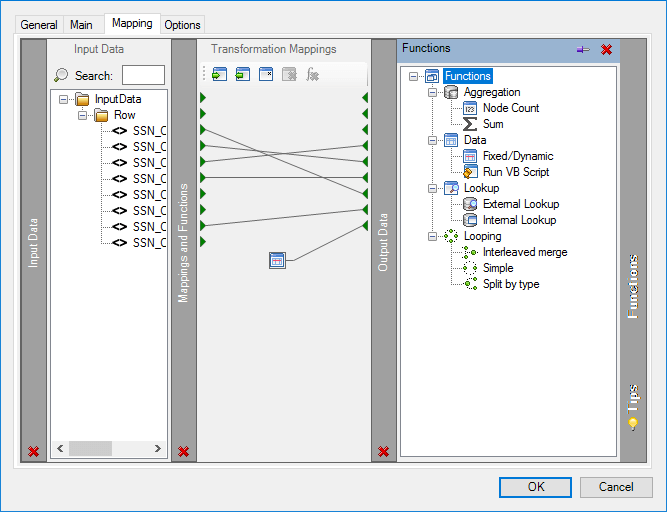
Aggregation Functions
Aggregation functions define operations for specific nodes.
![]() The Node Count Function
The Node Count Function
This function counts the number of occurrences of a node in the input recordset or XML document. The result is then passed to the mapped output node.
![]() The Sum Function
The Sum Function
This function calculates the total of the values from all iterations of an element in the input recordset or XML document. The sum of the values is used as the new value to an output element.
Data Functions
Data functions perform operations on input data to generate new output data.
![]() The Fixed/Dynamic Function
The Fixed/Dynamic Function
This function passes a static or dynamic value to the output XML schema. Use a variable or recordset column to generate the dynamic data.
![]() The Run VBScript Function
The Run VBScript Function
Use this function to perform VBScript operations to process input data, generate output data, or both.
Lookup Functions
Lookup functions are used to find values in a nominated source, by a key.
![]() The External Lookup Function
The External Lookup Function
Use this function to lookup values from an external database. This uses existing Database Query (ODBC) or Database Query (OLEDB) global connections.
![]() The Internal Lookup Function
The Internal Lookup Function
Use this function to find an alternative value for input data from a predefined lookup table.
Looping Functions
Looping functions loop through the input recordset or XML document to perform functions on all iterations of a node.
![]() The Interleaved Merge Function
The Interleaved Merge Function
This function loops through the input recordset or XML document and merges data from specified elements into a single occurrence for the mapped output data.
![]() The Simple Loop Function
The Simple Loop Function
This function loops through the input recordset or XML document and creates an output data node for every iteration of an input node it finds.
![]() The Split by Type Function
The Split by Type Function
This function is the opposite to the Interleaved Merge function in that it takes data from a single input node and splits it into two or more output data nodes.
About the Options Tab
The Options tab allows you to define how errors in this step are handled at task runtime.
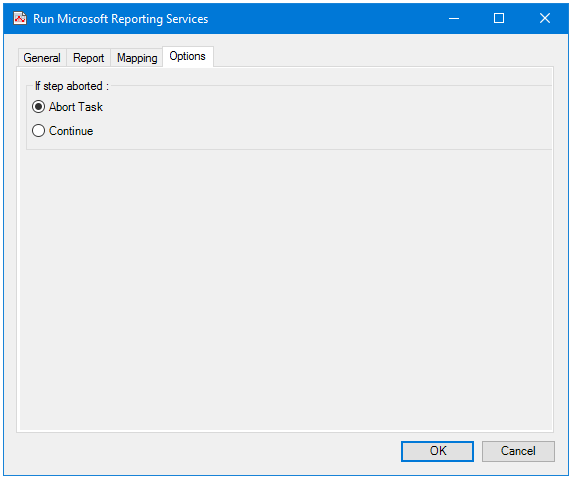
If the step is aborted, you can choose to Continue processing onto the next step in the task, or terminate the whole task immediately (Abort Task).